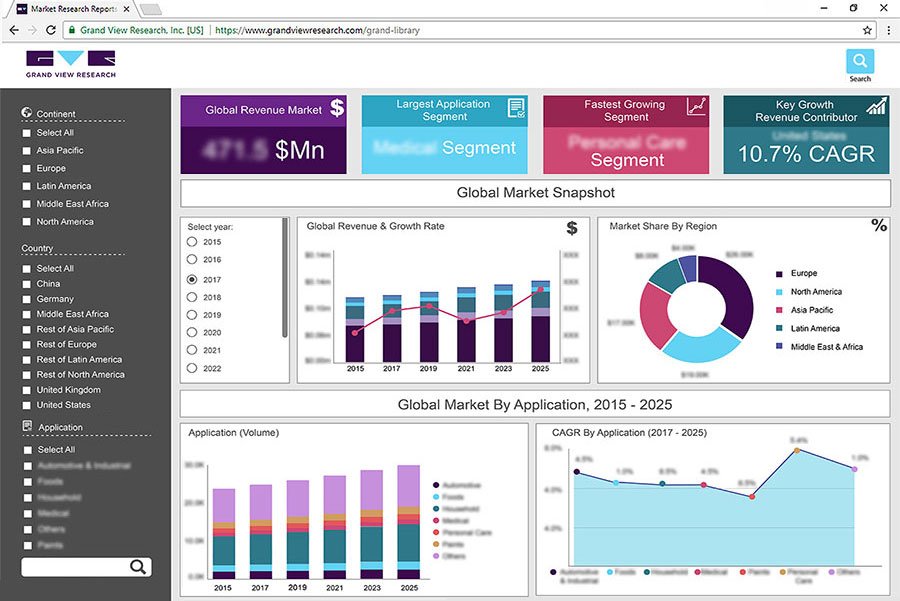
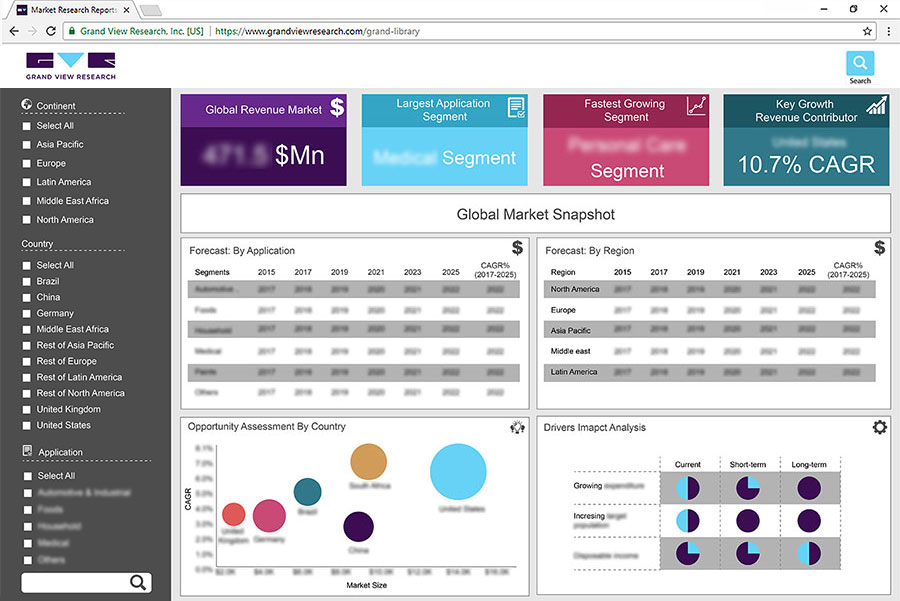
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) in the Textile industry
The non-financial parameters consisting of Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) have become a priority factor for business stakeholders contributing to the identification of materials risks and growth opportunities resulting in responsible investing. The integration of ESG in the Textile sector has rapidly increased since 2020, thereby delivering a real impact by maintaining and reducing its carbon footprint.
Prominent industry leaders in the Textile sector consider the ESG parameters a crucial factor in responsible sourcing and farming. It helps in the adoption of traditional methods to promote the community-based approach toward eco-friendlier ways of sustainable living, by enhancing their knowledge on issues of climate change and social responsibility.
According to the World Bank, the industry accounts for 10% of the annual global carbon emissions which is greater than the combined emissions from international flights and maritime shipping. This industry has also resulted in the utilization of 25 percent of all chemicals produced universally leading to the excessive release of chlorine, formaldehyde, along with heavy metals such as mercury and lead into various water bodies, thereby polluting them.
The textile industry has acquired a great deal of attention from investors interested in ESG impact investing. Alongside its significant impact on the environment, the apparel industry is also associated with significant impact on pace of production, labor practices, pollution, biodiversity impact, responsible resource use, and consumer sentiments. Thus, the market has significant attention from various stakeholders.
Key companies researched and analyzed in textile industry theme have built on this market position while adapting to several sustainable strategies resulting in a positive ESG impact within this sector.
ESG trends
The ‘E’ in the ESG – the Environmental parameter is a priority factor in this sector specifically appealing to consumers and investors. Companies in the textile industry promote carbon emergency by reducing or balancing their carbon footprint. Primarily, this industry focuses on minimizing resource use and reducing pollution in the supply chain to create a positive ESG impact. This includes areas such as agriculture, manufacturing, processing, fabric care, use, recycling, and disposal.
Including this, top companies and organizations in the Textile sector tend to create a positive cultural impact through ensuring safe labor practices. Companies in this industry also focus on considering the preferences of consumers to ensure they make informed decisions in addressing sustainability, alongside aiding the company’s profitability and growth.
The Textile industry also considers its efforts toward achieving various United Nations – Sustainable Development Goals (UN – SDGs). These include, but are not limited to Climate Action, Clean Water & Sanitation, Gender Equality, Responsible Consumption & Production, and Decent Work & Economic Growth. Furthermore,green sourcing in this industry helps in formulating new sustainability policies and processes for all operations while maintaining a regular monitoring system to ensure profitability in the future.
To extend this further, the adoption of the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) scheme is a significant step forward for producers with a responsibility covering – financial and physical, for the collection & disposal of post-consumer wastes that has elevated the ESG standards across the sector.
Multi-stakeholder engagement and collaboration could also result in improving awareness and knowledge with increased dialogues and discussions with governments, associations, buyers, and others about sustainability in this industry through responsible utilization of resources, switching to renewable forms of energy, and proper waste disposal techniques that could result in enhancement in reduction and recycling methods.
ESG Challenges
There are various challenges in the textile industry from the ESG point of view. Transformation from a low-cost ready-made clothing generating industry to a producer of products based on consumer sentiment is one of the key challenges. This would require improvement in innovative capacity while providing essential resources to maintain them, and acceleration in the development of technological fundamentals within the industry.
Besides this, the industry also faces major issues while stimulating additional investment in independent research and development through improving industry-institute collaborations. Concerning these, major companies within this industry that are a part of this thematic report, have strategies aimed at improving the processes of reduction and recycling to combat the effects of climate change.
Growth of The Textile Industry
According to a recent study by the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP), sustainability in the textile industry thrives on stronger governance practices within the sector, increasing finance towards environment-friendly techniques, and a determined step in the conversion of consumers’ consumption habits are vital for the textile industry to become more sustainable. The global textile market size as of 2020 was USD 1,000 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.4% between 2021 and 2028. The increasing rise of e-commerce platforms with the fashion sector’s proliferating demand for apparel is expected to enhance the market’s growth over the coming years as well as in terms of ESG.
Key Companies in this theme
• BSL Ltd.
• INVISTA Srl.
• Solvay S.A.
• Mayur Suitings
• Paramount Textiles
Scope of the Textile Industry ESG Thematic Report
• Macro-economic and ESG-variable analysis of the industry, including regulatory, policy, and innovation landscape
• Key insights on infrastructure developments and ESG issues affecting the theme
• Identify key initiatives and challenges within the industry
• Identify ESG leaders within the industry
• Understand key initiatives and the impact of companies within the sector to fuel an informed decision-making process
• Analysis of industry activities based on multi-media sources, including significant controversies and market sentiment
Key Benefits of Textile Industry ESG Thematic Report:
• Developing a comprehensive understanding of macro-economic, Policies & Regulations, and innovations affecting the textile sector, globally
• Key insights into Infrastructure developments and ESG issues affecting the theme
• Identifying ESG risks and opportunities for business among leading players in the industry
• Obtaining a clear and relevant understanding of company actions, progress, impact, and finding opportunities for investment in the sector